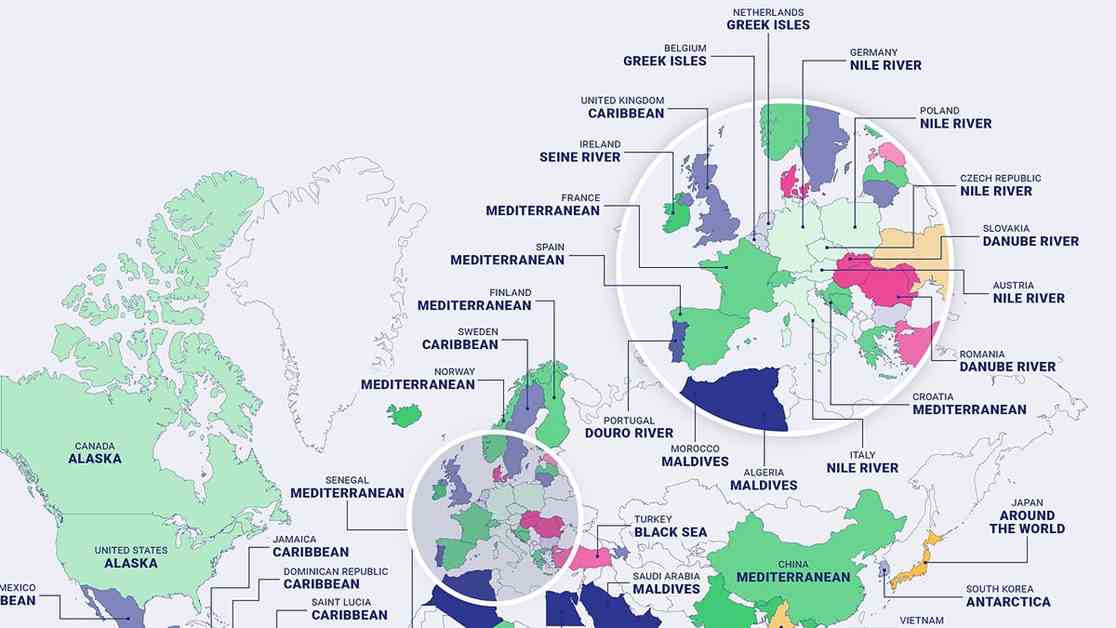
Map reveals the Caribbean as the globe’s No.1 destination for a cruise
A fascinating reworked world map reveals the most popular destination for a cruise for every country – and it’s the Caribbean that’s the globe’s favorite place for a trip on a ship. The map is color-coded to indicate each country’s favorite voyage, showing that the Caribbean is the most sought-after cruise destination of the year, with 2.8 million searches overall. It tops the wish lists of 44 countries around the globe, including the UK, Mexico, Jamaica, and Sweden.
The Mediterranean comes in as the second most popular cruise destination, with 2.1 million searches in the past 12 months. Countries like Spain, France, and Croatia are among those searching for this destination the most. An Alaskan cruise takes the third spot, with 1.8 million searches, being the top choice for residents of America and Canada.
The study conducted by cruise travel Insurance specialists AllClear also revealed that a cruise along the River Nile ranks fourth with one million searches, followed by Antarctica in fifth place with 969,670 searches. Sailing across the Norwegian fjords and a Danube River Cruise also made it to the top ten list.
Letitia Smith, Head of Communications at AllClear, expressed her fascination with the increasing interest in cruising holidays around the world, from the beautiful islands of Greece to the icy Antarctica. She emphasized the importance of cruise-specific travel insurance, which includes essential cover specific to cruise holidays such as onboard medical emergencies and missed port departures.
It’s clear that cruising offers a unique and unforgettable way to travel, with different destinations appealing to travelers from various countries. The allure of setting sail on the world’s oceans, seas, and rivers seems to be stronger than ever, as evident in the search trends for the most popular cruise destinations in each country.
To find out more about the research and the most sought-after cruise destinations across the world for 2024, visit: www.allcleartravel.co.uk/blog/where-the-world-wants-to-cruise/.